Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy treats cancer by using high-energy waves to kill tumour cells.
Technology In Cancer Treatment
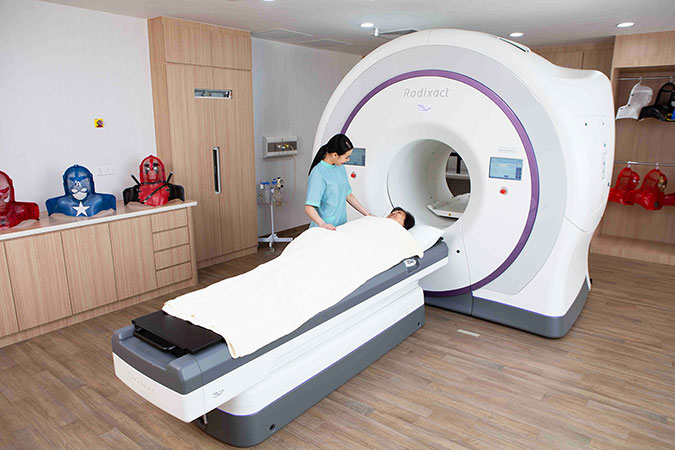
Sunway Medical Centre is proud to introduce Radixact-X9 Tomotherapy, the next-generation image-guided tumour treatment delivery system that uses refined x-ray beamline to provide unrivalled treatment precision to the patients.
See. Plan. Treat.
Radixact-X9 Tomotherapy provides a fully integrated platform for uniquely smart treatment planning, data management and treatment delivery.
| See | Plan | Treat |
|---|---|---|
|
With Data Management System Remote review of daily imaging Individual user privileges Disaster recovery features, including automatic backup and data mirroring |
With Treatment Planning System Dose calculation on a single treatment planning workstation Treatment plan comparison Auto segmentation of head and neck, brain, pelvis Precise Adaptive Radiation Therapy |
With Treatment Delivery System Real-time motion synchronisation Dose sculpting mode Continuous 360-degree treatment delivery |
Versatility in action.
Real-time monitoring.
Designed to accommodate all forms of patient and tumour motion with daily imaging, Radixact-X9 Tomotherapy uses real-time imaging to guide the treatment each day, allowing doctors to adjust patient treatment based on even the smallest changes in patient anatomy continually.
Game-changing precision.
Radixact-X9 Tomotherapy enables continuous delivery from 360 degrees around the patient with highly conformal and homogeneous dose to the tumour. A clinician can also deliver treatment from specific fixed angles, shaping the radiation to the tumour while sparing healthy tissue.
Intelligent treatment planning and delivery.
A uniquely smart radiation therapy system, Radixact-X9 Tomotherapy is designed to deliver scalable, highly precise treatment for patients with a variety of individual clinical needs. The automated adaptive radiation therapy also allows clinicians to easily identify patients that require treatment re-planning, taking treatment precision to entirely new levels.
Revolutionary treatment customised to suit your needs.
Using a refined x-ray beamline and next-generation imaging technology, Radixact-X9 Tomotherapy is built to provide unprecedented flexibility in providing personalised treatment for a wide range of possible indications.
Schedule an appointment with us. Now.
At Sunway Medical Centre, we equip our medical team with the latest technologies and treatment systems to deliver value-based care and treat a wide range of indications with high-quality outcomes. We are here to understand your specific needs and customise the radiotherapy treatment plan for you accordingly. Make an appointment with your treating oncologist now to determine the type of treatment that is best suited to your condition.
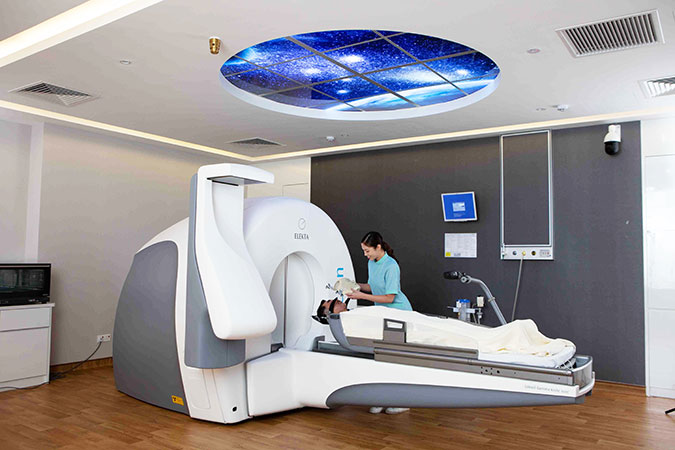
The Leksell Gamma Knife® Icon™ is a clinically proven method to treat intracranial (within the skull) locations – such as the brain, brain stem or the trigeminal nerve. Despite its name, the Leksell Gamma Knife® Icon™ does not involve a surgical incision or opening of the skull, but highly sophisticated non-invasive treatment that uses a beam of radiation to damage targeted tissue in a very precise manner while minimising exposure to healthy surrounding tissues and critical structures.
This highly precise and focused treatment is called stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS). SRS reduces the risk of potential side effects that might impact normal brain function and your quality of life.
Your neurosurgeon or clinical oncologist will determine the type of treatment you receive, based on your diagnosis and your specific treatment needs. For many indications, the Leksell Gamma Knife® Icon™ treatment is delivered in a single session. For others, you may be offered fractioned stereotactic surgery, which divides the total radiation dose over several treatment sessions.
Fractionation extends the Leksell Gamma Knife® Icon™ precision and accuracy to previously challenging tumours, including large lesions or those abutting very sensitive areas such as the optic chiasm (where the left and right optic nerves partially cross to the opposite side of the brain).
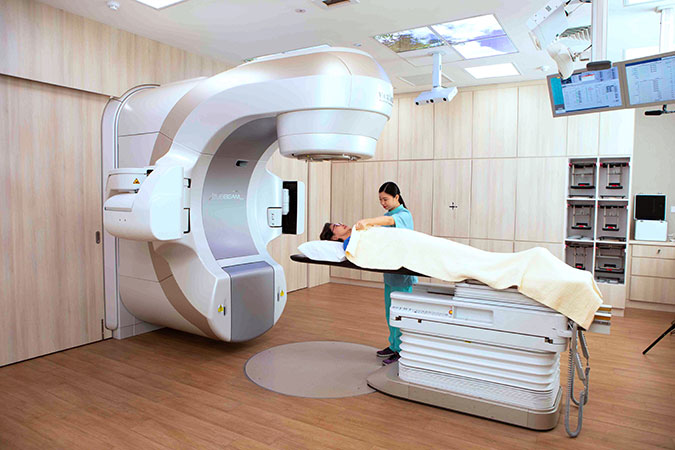
The Varian TrueBeam™ STx technology is a revolutionary innovation in cancer treatment. It expands radiotherapy treatment options for even the most challenging cancer cases in the lung, breast, head and neck, abdomen, liver and other regions.
The system uses sophisticated 3D imaging to target and treat tumours of all shapes, sizes and locations with pinpoint accuracy. Images can be generated using 25% less X-ray dose. These images are used to fine-tune a patient’s position prior to and during the treatment process.
The precision of the system is measured in increments of less than a millimetre. This accuracy is made possible by the system’s sophisticated architecture, which synchronises imaging, patient positioning, motion management, beam shaping and dose delivery. The system performs accuracy checks every ten milliseconds throughout the entire treatment.
Linear accelerator radiation therapy (LINAC) is a form of external-beam radiation therapy that uses electricity to deliver high energy radiation that is used to treat cancer. Its unique feature is its ability to customise the rays to conform to a tumour’s shape and destroy cancer cells while sparing surrounding normal and healthy tissue. Radiotherapy has proven to be an effective treatment for a wide variety of clinical problems, and the linear accelerator radiation therapy could be used to treat all areas of the body, from head to toe.
Linear accelerator for cancer treatment is a good choice for those who prefer a pain-free and safe treatment option. The built-in safety feature in the linear accelerator radiation therapy is to ensure that the dose delivered does not exceed the dose prescribed, and the entire treatment process is constantly monitored by a certified and experienced medical physicist.
Choosing linear accelerator for cancer treatment is a smart and effective decision a cancer patient could make. Today, it is one of the most widely used cancer treatment modalities in many parts of the world, and is available at Sunway Medical Centre.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is a highly targeted and highly effective way to destroy cancer cells. Radiation therapy is a localised treatment which only affects the part of your body that requires treatment. High-energy X-rays and gamma rays are some of the types of radiation therapy used for cancer treatment.
Radiation therapy may be delivered by a machine outside the body (external-beam radiation therapy), or it may come from radioactive material placed in the body near cancer cells (internal radiation therapy, also called brachytherapy).
Despite what many people fear, radiation therapy is relatively easy to tolerate and its side effects are limited to the treated area.
About half of all cancer patients receive some form of radiation therapy sometime during their treatment. Most of the time radiation therapy needs to be delivered over several days or weeks. Most of our patients spend about half an hour each day, and are otherwise able to maintain their usual activities.
Types of Radiation Therapy
In external radiation therapy, a machine called a linear accelerator (LINAC) directs a beam of radiation through the skin of the tumour. The machine does not touch you but rotates around you, sending delivering radiation to your body from different directions. With the use of state-of-the-art treatment techniques and equipment, high dosage of radiation is aimed and shaped according to the contour of your tumour which ensures the dose to your surrounding healthy tissues and kept at a minimum.
3-Dimensional Conformal Radiation Therapy (3D-CRT) delivers a conformal radiation dose from different directions to the tumour, while sparing surrounding normal structures.
Conformal Radiation Therapy uses a specialised planning CT scanner and sometimes other scans, such as MRI scans. This means the treatment team can plan the radiotherapy treatment area very precisely in 3 dimensions – width, height and depth.
Intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) is an advanced type of conformal radiation therapy. It uses sophisticated software and hardware to vary the shape and intensity of radiation delivered to different parts of the treatment area. It is one of the most precise forms of external beam radiation therapy available. It is very helpful in areas such as the head and neck, for example to avoid the spinal cord or salivary glands.
Volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) is a type of IMRT and works by delivering a continuous beam of radiotherapy in an arc which moves around the tumour, changing the beam shape and treatment dose automatically as it moves.
Treatment sessions with VMAT are significantly shorter, reducing patient discomfort and patient movement during prolonged treatment.
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS), sometimes called radiosurgery, involves the delivery of a high dose of focused radiation therapy to a small, well-defined area in the brain or other part of the head. This is usually delivered in one, or few treatment sessions.
Despite the name, SRS does not involve actual surgery. It is called ‘surgery’ because a result similar to an actual surgical procedure is created by one therapy session. It is a non-invasive treatment for some patients with tumours or cancers of the brain and head.
SRS may be used to treat patients with secondary cancers that have moved spread to the brain (brain metastasis), slow growing benign tumours (such as acoustic neuromas), and sometimes to re-treat an area that has previously had radiation therapy before (head and neck cancers or primary brain cancers). In addition, SRS can also be used to treat some non-cancer or tumour conditions such as arteriovenous malformations (abnormal connection of veins and arteries) and complex cases of trigeminal neuralgia.
When SRS is used to treat body tumours, it’s called stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT). SBRT can deliver very high doses of radiation over a relatively short total treatment time resulting in an increased probability of local tumour control. This advanced technology treatment can be applied for the treatment of small lung cancers and control of liver tumours and selected spinal metastases.
Image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) is the use of imaging during radiation therapy to improve the precision and accuracy of treatment delivery. IGRT is used to treat tumours in areas of the body that move, such as the lungs. Radiation therapy machines are equipped with imaging technology to allow your doctor to image the tumour before and during treatment. By comparing these images to the reference images taken during CT simulation, the patient’s position and/or the radiation beams may be adjusted to more precisely target the radiation dose to the tumour. Some IGRT procedures may use fiducial markers, to help align and target the lesion.
Brachytherapy is a procedure that involves placing radioactive material inside your body to treat cancer. It allows your doctor to use a higher total dose of radiation to treat a smaller area in shorter time than conventional external beam radiation therapy (EBRT).
Brachytherapy is shown to be effective in combination with external beam radiotherapy and chemotherapy. The accurate delivery of radiation directly to the tumour inside the body reduces the risks of side effects.
Brachytherapy can be given over a short period of time – often a matter of day and is an established, treatment. However, it is continually being advanced with the very latest technology to provide even more effective treatment.
Intraoperative radiation therapy (IORT) delivers a concentrated dose of radiation therapy to a tumour bed during surgery. This advanced technology may help kill microscopic disease, reduce radiation treatment times or provide an added radiation "boost."
This innovative therapy is administered at the time of surgery, following cancer removal. Typically, standard radiation therapy involves five days of treatment per week, for a total of five to six weeks for some patients. With IORT, clinical oncologists can deliver a similar dose of radiation in a single treatment session, while also preserving healthier tissue. This helps to reduce side effects and the time spent going back and forth to the hospital for radiation treatments.
A patient must be a surgical candidate to be eligible for IORT. Do consult with your oncologist to find out if you fit the criteria.
General side effects
Every individual responds and reacts differently to radiotherapy. Given this, radiotherapy affects each one differently. Some people may have mild side effects and others encounter more severe side effects. The side effects can range from medium short term to long term, depending on the individual and the cancer affected.
Some of the main side effects experienced by patients include:
Feeling tired
One main side effect is fatigue or feeling tired and weak after treatment, more so if patients undergo treatment over several weeks. Tiredness could also be due to low levels of red blood cells (anaemia).
Feeling an overall weakness is also common, and this may last for a few weeks post-treatment. Patients are encouraged to rest well and try to exercise a little when they can.
Skin issues
Some patients complain of sore skin in the area being treated. The skin may look reddened or darker than usual. It may also get dry and itchy. Breakouts and blisters may also form around the treated skin area. Our teams will advise you on the best way of coping with this.
Hair loss
One side effect that most patients are concern of is hair fall. Some patients may experience hair fall out in the treatment area. Hair in other parts of the body is not affected. The hair should begin to grow back again a few weeks after the treatment ends.
Eating problems
Radiation to the mouth or throat, or parts of the digestive system (like the stomach or intestines) may cause eating and digestion problems. For instance, you may have sores in your mouth or throat, nausea, vomiting, or loss of appetite.
However, patients are encouraged to eat proteins and some high-calorie foods during this time to help the body recover. Experts have found that patients who eat well can better handle cancer treatment and side effects.
