Nasopharyngeal Cancer
Screening Guidelines
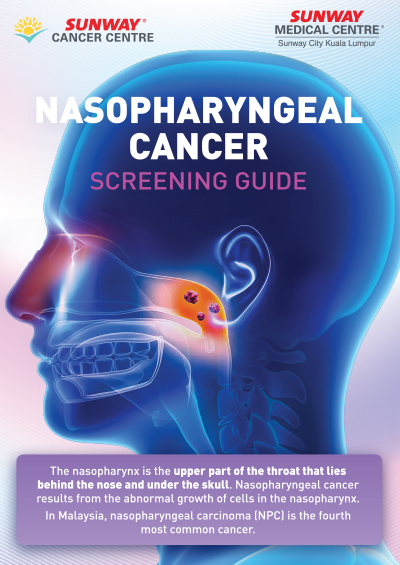
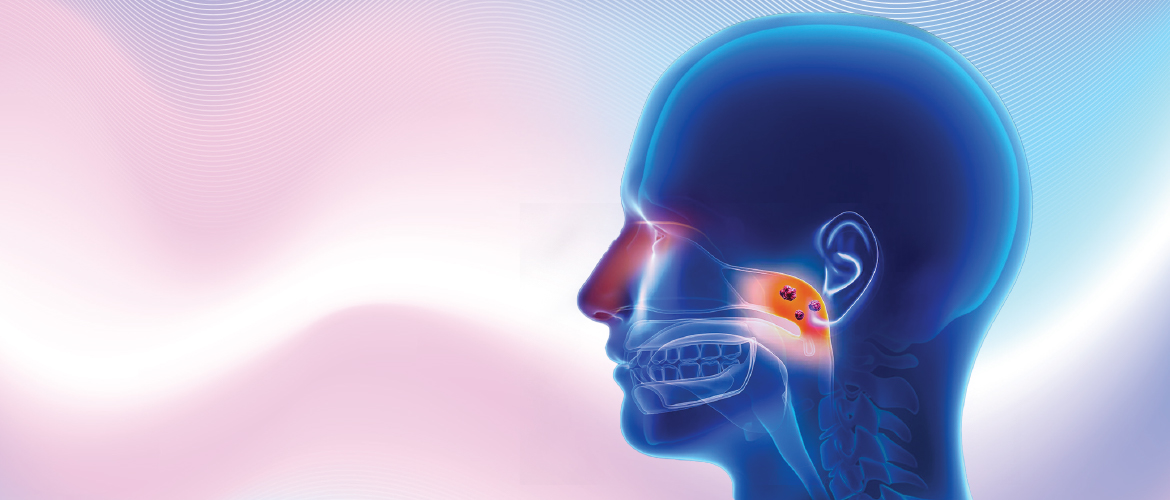
The nasopharynx is the upper part of the throat that lie behind the nose and under the skull. Nasopharyngeal cancer results from the abnormal growth of cells in the nasopharynx.
In Malaysia, nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is the fourth most common cancer.
What is The Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)?
Nasopharyngeal Cancer Risk Factors
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection
Family history of nasopharyngeal cancer
High intake of preserved, salted or
fermented food or fruit
Smoking

Occupational exposure to wood dust,
chemicals, dust, exhaust or smoke

Individuals of Southern
Chinese descent
Nasopharyngeal Cancer Signs and Symptoms
Painless neck lump(s)

Blocked nose

Double vision

Headache

Nose bleed or bloodstained phlegm, especially upon waking up in the mornings

Facial numbness
Sore throat
Unilateral ear pressure or ringing sound in the ear
Screening & Diagnosis Options
EBV DNA |
|
The EBV DNA test is a diagnostic test used to detect the presence of EBV genetic material (DNA) in a person’s blood. PURPOSETo determine if a person is currently infected with EBV. PROCEDUREA blood sample will be taken, and the DNA from the virus will be analysed. INTERPRETATIONPositive Result: Negative Result: |
EBV VCA-IGA
|
|
The EBV VCA-IgA antibody test detects specific antibodies produced by the immune system in response to the EBV viral capsid antigen (VCA). PURPOSE
PROCEDUREA blood sample will be collected. INTERPRETATIONIgA Antibodies Present: IgA Antibodies Absent: |
|
|
NASAL Endoscopy |
A nasal endoscopy is a diagnostic procedure that allows a doctor to examine the inside of the nasal passages and sinuses using |
|
PURPOSETo evaluate nasal and sinus conditions (e.g., nasal polyps, tumours). |
PROCEDURE
|
NASAL Endoscopy |
A nasal endoscopy is a diagnostic procedure that allows a doctor to examine the inside of the nasal passages and sinuses using |
PURPOSETo evaluate nasal and sinus conditions (e.g., nasal polyps, tumours). PROCEDURE
|
Nasopharyngeal Cancer Treatment Options

Radiotherapy
Mechanism:
Uses high-energy beams to kill cancer cells or slow their growth.
Target:
Nasopharynx and neck lymph nodes
Effectiveness:
Commonly used for early-stage NPC and in combination with chemotherapy for more advanced stages.

Chemotherapy
Mechanism:
Anti-cancer drugs destroy cancer cells.
Administration:
Intravenous
Effectiveness:
Often combined with radiation therapy to potentiate the action of radiation.

Surgery
Indication:
Used if cancer recurs or persists after initial treatment.
Procedure:
Removal of the main tumour and affected lymph nodes.
Nasopharyngeal Cancer
Screening Guidelines
Click to Download PDF