Colorectal Cancer Screening Guidelines
Colorectal cancer is the 2nd most common cancer in Malaysia. It is also highly treatable if caught early.
Learn more about the risk factors, sign, symptoms and how you can get screened.
Should you get screened?
It depends on your medical condition and family history.
You can check whether you need to screen for colorectal cancer by the following flowchart below.


A first relative (parent, sibling or child) with colorectal cancer, familial adenomatous polyposis or Lynch syndrome?
OR
A history of ulcerative colitis, Crohn disease or colorectal polyps?
| Yes | Discuss with your doctor on when you can start colonoscopy screening | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| No | Are you 45-75 years old? | ||
 |
Yes | No | |
|
Perform Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT) annually, and stop screening at age 75. If result is positive, a colonoscopy screening should be performed. |
Below 45 Years Above 75 Years Old |
||
| Yes | |
|---|---|
| Discuss with your doctor on when you can start colonoscopy screening | |
| No | |
| Are you 45-75 years old? | |
 |
|
| Yes | |
| Perform Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT) annually, and stop screening at age 75. If result is positive, a colonoscopy screening should be performed | |
| No | |
|
Below 45 Years Above 75 Years Old |
Signs & Symptoms of Colorectal Cancer
















Screening Options

1) Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is a procedureb which is done with a flexible camera (scope) to look for abnormalities inside the rectum and colon
%
Cancer detection rate
%
Polyp detection rate
2) Fecal-Immunochemical Test (FIT)
FIT is a test that checks for presence of blood in the stool
%
Cancer detection rate
%
Polyp detection rate

Screening Options

1) Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is a procedureb which is done with a flexible camera (scope) to look for abnormalities inside the rectum and colon
%
Cancer detection rate
%
Polyp detection rate

2) Fecal-Immunochemical Test (FIT)
FIT is a test that checks for presence of blood in the stool
%
Cancer detection rate
%
Polyp detection rate
What is a Colonoscopy?
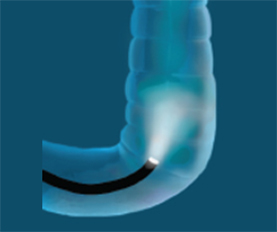
Step 1
A long thin tube with an attached camera will be inserted into your rectum and move through the entire colon, allowing your doctor to view the insides of your rectum and colon on a screen.
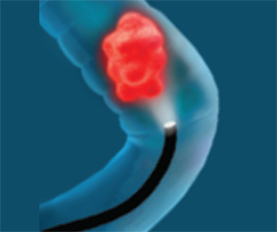
Step 2
During this procedure, polyps or other types of abnormal tissue can be removed through the scope. Tissue samples can be taken to be sent to the lab for testing as well.

Step 3
The entire procedure takes around 30-60 Minutes.

Step 4
Your Doctor will then review the result of the colonoscopy and then share the results with you.
What is a Colonoscopy?

Step 1
A long thin tube with an attached camera will be inserted into your rectum and move through the entire colon, allowing your doctor to view the insides of your rectum and colon on a screen.

Step 2
During this procedure, polyps or other types of abnormal tissue can be removed through the scope. Tissue samples can be taken to be sent to the lab for testing as well.

Step 3
The entire procedure takes around 30-60 Minutes.

Step 4
Your Doctor will then review the result of the colonoscopy and then share the results with you.
What is the process of Fecal-immunochemical Test (FIT)?

Deposit a stool sample on top of the collection paper and use the probe to scrape the surface of the stool.
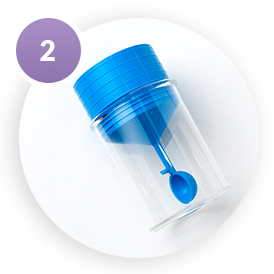
Place the probe with stool sample back in the collection tube.

Place the collection tube in the biohazard bag and return to the lab within 48 hours of collecting your sample.
The FIT test will check for the presence of small amounts of blood in your stool.
What is the process of Fecal-immunochemical Test (FIT)??

Deposit a stool sample on top of the collection paper and use the probe to scrape the surface of the stool.

Place the probe with stool sample back in the collection tube.

Place the collection tube in the biohazard bag and return to the lab within 48 hours of collecting your sample.

The FIT test will check for the presence of small amounts of blood in your stool.
Colorectal Cancer Screening Guide
Click To Download PDF