Cervical Cancer Screening Guidelines
Cervical cancer is caused largely by the Human papillomavirus (HPV). Find out how you can get screened and protected today.
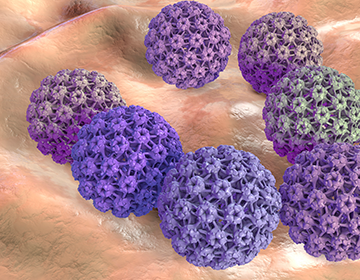
What is Human
Papillomavirus (HPV)?
HPV is a group of more than 100 different types of viruses.
Most are harmless, HPV-18. but some cause genital warts and others cause changes that lead to cancer.
About 70% of HPV-related cervical cancer is caused by HPV-16 or most are harmless, HPV-18.
Cervical Cancer Risk Factors





Signs & Symptoms Of Cervical Cancer

Pain during sexual intercourse

Bleeding after menopause
Bleeding after intercourse
Heavy menstrual bleeding
Light bleeding or blood spots between periods

Excessive vaginal discharge

Unexplained back pain/pelvic pain

Unexplained weight loss
Screening Option
1) Pap Smear
A procedure that uses a small brush to collect cells from the surface of the cervix. The cells are viewed under a microscope to find out if they are abnormal.
2) HPV DNA Test
It is a laboratory test that is used to detect the DNA of High Risk HPV infection. It can be done using the sample of cells removed during a Pap smear test.
3) HPV Self-sampling
Sample for a HPV test can also be collected by the patient with a self sampling tool and is sent back to the lab for testing of abnormalities.
Cervical Cancer Screening Guideline
Age 21 - 29
- Pap smear for all women between the ages of 20 and 65 years old or who have been sexually active.
- If two consecutive year tests are negative, subsequent screening can be done every three years.
- HPV testing is not recommended

Age 30 - 65
- Have a co-test (a Pap smear and an HPV test together) every 5 years, or
- If HPV is negative

If you are experiencing any symptoms,
visit a gynaecologist for a consultation.
Cervical Cancer Screening Guide
Click To Download PDF
